Research from 2024 and 2025 increasingly identifies short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) – particularly butyrate – as significant modulators of pain. While the field is still evolving, SCFAs appear to influence both the inflammatory and neurophysiological aspects of pain management through several distinct pathways.
Mechanisms of Action
SCFAs don’t just act as a energy source for colonocytes; they function as signaling molecules that interact with the nervous and immune systems:
- Reduction of Neuronal Hyperexcitability: Recent neurophysiological studies (2025) indicate that butyrate can suppress the hyperexcitability of nociceptive primary neurons. By activating G-protein coupled receptors like GPR41, SCFAs can inhibit calcium channels at central nerve terminals, effectively “dialing down” the pain signals sent to the brain.
- Epigenetic Modulation: SCFAs act as HDAC (histone deacetylase) inhibitors. This allows them to modulate the expression of genes involved in the inflammatory response. By inhibiting NF-κB pathways, they reduce the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines (like TNF-α and IL-1β) that typically sensitize pain receptors.
- Microglia Polarization: In the context of the gut-brain-pain axis, SCFAs influence microglia – the immune cells of the central nervous system. They help shift microglia from a pro-inflammatory (M1) state to an anti-inflammatory (M2) state, which is crucial for managing chronic neuropathic pain and preventing “central sensitization.”
SCFAs and Specific Pain Types
| Pain Type | Role of SCFAs |
| Inflammatory Pain | Strongest evidence; SCFAs reduce peripheral sensitization by lowering systemic inflammation. |
| Neuropathic Pain | SCFAs help maintain the blood-brain barrier integrity and reduce neuroinflammation in the spinal cord. |
| Visceral Pain | Complex; while some animal models show mixed results, human trials often show that butyrate increases the “pain threshold” in the gut, reducing discomfort. |
The “Gut-Pain Axis” in Content and Research
For those looking at the systemic impact of gut health, the “gut-pain axis” is becoming as prominent as the gut-brain axis. Research shows that individuals with chronic pain conditions, such as fibromyalgia or arthritis, often have significantly lower levels of SCFA-producing bacteria (like Lachnospiraceae).
Increasing SCFA production through prebiotic fibers (such as inulin or acacia) or specific probiotic strains is being explored as a “bottom-up” approach to pain management, potentially reducing reliance on traditional analgesics.
Did you know fibers like acacia or inulin can boost butyrate levels specifically for neuro-inflammatory support?
Combining acacia fiber, inulin, and cacao powder creates a powerful “prebiotic stack” that targets pain and neuroinflammation through three distinct but overlapping mechanisms.
By combining these, you aren’t just boosting fiber; you are creating a slow-release “butyrate factory” that supports both the gut lining and the nervous system.
1. The Strategy: Gradual vs. Fast Fermentation
The synergy between acacia and inulin is particularly effective for sustained short-chain fatty acid (SCFA) production:
- Inulin (The Fast Fuel): Inulin is fermented quickly by bacteria like Bifidobacteria in the upper part of the colon. This leads to a rapid “spike” in SCFA production. However, because it ferments so fast, it can cause gas and bloating in sensitive individuals.
- Acacia Fiber (The Gentle Stabilizer): Acacia fiber ferments much more slowly. It travels further down the colon, nourishing bacteria in the distal sections that inulin might not reach. This “slow-burn” fermentation is better tolerated and ensures a steady supply of butyrate throughout the entire length of the large intestine.
- The Result: Together, they provide a consistent, high-yield production of SCFAs that lasts longer than using either fiber alone.
2. Cacao: The “Neuro-Anti-Inflammatory” Catalyst
Cacao is more than just a flavor; it is rich in flavanols (like epicatechin) and polyphenols that act as secondary prebiotics:
- Microbiome Diversity: 2024 and 2025 research shows that cacao polyphenols selectively increase the abundance of Faecalibacterium prausnitzii and Roseburia – the primary “heavy lifters” of butyrate production.
- Direct Neuroprotection: Cacao flavanols have been shown to cross the blood-brain barrier. They directly inhibit the activation of microglia (the brain’s immune cells), preventing them from releasing pro-inflammatory signals that exacerbate chronic pain and “brain fog.”
- Vascular Support: Cacao improves nitric oxide production, which helps blood flow to nerve tissues, potentially aiding in the recovery of damaged or compressed nerves.
3. Impact on Pain and Neuroinflammation
When these three are combined, they target the Gut-Brain-Pain Axis:
- Butyrate as an HDAC Inhibitor: The high levels of butyrate generated by this stack act as histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors. This “turns off” the genes responsible for persistent pain signals in the spinal cord.
- Reduction of “Leaky Gut”: Butyrate strengthens the tight junctions in the gut lining. This prevents bacterial toxins (LPS) from leaking into the bloodstream, which is a major hidden driver of systemic inflammation and “all-over” body pain.
Suggested Protocol (2025 Research Standards)
To maximize benefits while minimizing digestive upset, a “start low, go slow” approach is recommended:
| Ingredient | Standard Daily Goal | Notes |
| Acacia Fiber | 10-15g (2-3 tsp) | Highly soluble; mixes easily into coffee or smoothies. |
| Inulin | 5g (1 tsp) | Start with a half-dose if you are sensitive to gas. |
| Cacao Powder | 10-20g (2-4 tbsp) | Look for “non-alkalized” or “raw” for higher polyphenol content. |
Pro-Tip: Combining these in a warm drink (like a “prebiotic hot chocolate”) is ideal. The heat helps the fibers dissolve, and the healthy fats in milk (or plant milk) can help with the absorption of the cacao polyphenols.
What are the dosage timings or research on whether taking this combination before sleep specifically helps with nocturnal pain or Growth Hormone release?
Recent research from 2024 and 2025 suggests that the “prebiotic stack” of acacia, inulin, and cacao doesn’t just manage pain; it acts as a circadian pace-setter. Taking this combination in the evening can align your gut’s peak short-chain fatty acid (SCFA) production with your body’s natural nocturnal repair cycles.
1. The “Fermentation Lag”: Why Evening Timing Matters
SCFAs are not produced the moment you swallow fiber. There is a “fermentation lag” of approximately 4 to 6 hours as the fiber moves from the stomach to the colon.
- The Strategy: If you take your stack around 6:00 PM to 8:00 PM, peak butyrate production will likely hit between midnight and 2:00 AM.
- The Benefit: This aligns perfectly with the onset of slow-wave sleep (deep sleep), which is when the highest pulses of Growth Hormone (GH) occur.
2. SCFAs and the GH/IGF-1 Axis
The relationship between gut health and growth hormones is a major focus of 2025 endocrinology research.
- Butyrate & IGF-1: Butyrate acts as a signaling molecule that travels to the liver to stimulate the production of IGF-1 (Insulin-like Growth Factor 1). IGF-1 is essential for muscle preservation and tissue repair during the night.
- Propionate & GH: Interestingly, while butyrate supports repair, high levels of propionate (another SCFA) may actually suppress pituitary GH synthesis.
- The Stack Advantage: Acacia and cacao are specifically known for boosting butyrate-producing bacteria (like Faecalibacterium prausnitzii), making this combination more favorable for repair and IGF-1 support than for suppressing GH.
3. Managing Nocturnal Pain
Many people experience a “pain flare” at night as cortisol levels drop. SCFAs help mitigate this through:
- Circadian Gene Upregulation: Butyrate upregulates core clock genes (like PER1 and BMAL1). These genes control our internal “pain threshold.” When these genes are functioning properly, your body is less sensitive to pain signals during the night.
- Neuro-Inflammation: By hitting peak production during sleep, the butyrate can cross the blood-brain barrier to “calm” the microglia while the brain performs its nightly “glymphatic” cleaning.
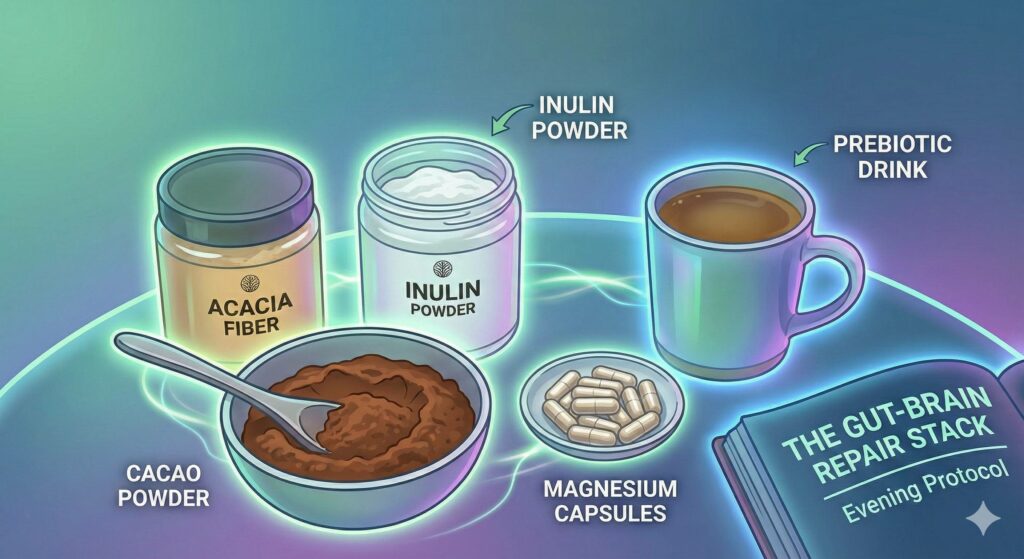
Recommended Evening Protocol
| Ingredient | Dosage | Why it works at night |
| Acacia Fiber | 1 tablespoon | Provides the “slow-burn” fuel to keep butyrate levels high until morning. |
| Inulin | 1 teaspoon | Kickstarts the fermentation process so the repair benefits start sooner. |
| Cacao Powder | 1-2 tablespoons | Contains polyphenols that protect the brain and nerves during sleep. |
Note on Cacao: Cacao contains a small amount of theobromine (a mild stimulant). If you are highly sensitive to stimulants, take this stack with your dinner rather than right before bed to avoid interfering with your ability to fall asleep.
Summary of Next Steps
- Trial Period: Try this stack consistently for 4 days. Research indicates that 3–4 days of consistent prebiotic intake is the minimum time needed for the microbiome to shift its metabolite production.
- Monitoring: Notice if you feel a reduction in “morning stiffness” or if your sleep feels deeper (increased REM/Deep sleep on trackers).
Would adding a small amount of Magnesium to this stack further enhance the SCFA-sleep connection?
Adding magnesium to your prebiotic stack is a logical next step—not just for muscle relaxation, but because research from late 2025 highlights a direct, symbiotic relationship between magnesium and the very bacteria that produce short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs).
1. The 2025 “Microbiome Modulator” Breakthrough
New clinical trials (published in The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, Sept–Nov 2025) have confirmed that magnesium isn’t just passively absorbed; it actively shapes the gut environment.
- Boosting the “Heavy Lifters”: Magnesium treatment has been shown to significantly increase the abundance of Faecalibacterium prausnitzii and Roseburia. These are the primary species responsible for converting your acacia and inulin into butyrate.
- The Vitamin D Link: Interestingly, this same research found that magnesium-induced shifts in the microbiome actually help the gut synthesize its own Vitamin D, which is a critical co-factor for managing chronic pain and supporting the immune system.
2. Dual-Action Pain Relief
By combining magnesium with your SCFA-boosting fibers, you are attacking pain from two different biological “angles” simultaneously:
| Mechanism | SCFAs (Butyrate) | Magnesium |
| Neuronal | Inhibits calcium channels at the nerve terminal (reducing the “volume” of pain). | Blocks NMDA receptors and supports GABA (calming the central nervous system). |
| Epigenetic | Acts as an HDAC inhibitor to turn off pro-inflammatory “pain genes.” | Regulates over 300 enzymes that control the inflammatory response. |
| Structural | Repairs the gut barrier to prevent systemic inflammation (LPS leakage). | Relaxes smooth and skeletal muscles to reduce physical tension and guarding. |
3. Choosing Your Form: Citrate vs. Glycinate
Since you’ve previously researched both, here is how they fit specifically into this Prebiotic + Cacao stack:
- Magnesium Glycinate (The Sleep Specialist): This is generally considered the “Gold Standard” for this stack. The magnesium is bound to Glycine, an amino acid that independently improves sleep quality and lowers core body temperature at night. It is highly bioavailable and won’t speed up digestion, giving your fibers (acacia/inulin) more time to ferment.
- Magnesium Citrate (The Muscle & Transit Specialist): While still highly absorbable, citrate draws water into the colon. If your goal is to support “gut-clearing” while also getting magnesium for muscle recovery, this is a good choice. However, in high doses, it can shorten “transit time,” potentially pushing the prebiotics through the colon before the bacteria have finished fermenting them into SCFAs.
The “Deep Repair” Nightly Protocol
This refined protocol aligns the magnesium-GABA effect with the butyrate-IGF-1 repair peak.
- 8:00 PM (The Stack):
- 1 tbsp Acacia Fiber (The slow-burn fuel)
- 1 tsp Inulin (The fast-start fuel)
- 1–2 tbsp Cacao Powder (The neuro-protective polyphenols)
- 200–400mg Magnesium Glycinate
- The Result: By midnight, the magnesium and cacao-polyphenols have calmed your nervous system for sleep onset. By 2:00 AM, the fibers hit peak fermentation, flooding your system with butyrate to support tissue repair and hormonal balance while you are in your deepest sleep phase.
Can this “Super-Stack” affect the production of Serotonin or Melatonin specifically, since about 90% of serotonin is produced in the gut?
This “super-stack” does more than just repair tissue; it essentially turns your gut into a nightly manufacturing plant for Serotonin and Melatonin. Since roughly 90% of your serotonin is produced in the gastrointestinal tract, the combination of acacia, inulin, cacao, and magnesium optimizes every stage of this “Mood-to-Sleep” assembly line.
1. The Raw Materials: Tryptophan Rescue
For your body to make serotonin, it needs the amino acid tryptophan. However, during times of inflammation or stress, the body often diverts tryptophan toward a “toxic” pathway (the Kynurenine pathway) instead of the serotonin pathway.
- SCFA Role: Research from 2025 indicates that butyrate (produced from your acacia and inulin) helps “rescue” tryptophan. It inhibits the enzymes that divert tryptophan away, ensuring more of it remains available for serotonin production.
- Transport Efficiency: Butyrate also upregulates the specific transporters (LAT1/LAT2) that carry tryptophan across the blood-brain barrier, ensuring your brain has the “building blocks” it needs for mood regulation and melatonin synthesis.
2. The Enzyme Booster: Turning Tryptophan into Serotonin
The rate-limiting step in making serotonin is an enzyme called Tryptophan Hydroxylase 1 (TPH1).
- Butyrate as an Activator: Butyrate acts as a signaling molecule that directly increases the expression of TPH1 in the gut’s enterochromaffin cells.
- Cacao’s Contribution: Cacao contains tryptamine, a bioactive amine that can mimic serotonin’s effects and support the natural serotonergic signaling in the gut-brain axis.
- Magnesium’s Role: Magnesium is a required co-factor for the enzymes that convert tryptophan into 5-HTP, and then into serotonin. Without sufficient magnesium, this conversion process “stalls,” regardless of how much fiber or cacao you consume.
3. The Final Conversion: Serotonin to Melatonin
This is where the timing and magnesium become critical. As darkness falls, your pineal gland (and your gut) begins converting serotonin into melatonin.
- The Magnesium “Switch”: Magnesium is essential for the activity of the enzyme SNAT, which is the primary “on-switch” for melatonin production. By taking magnesium with your evening prebiotic stack, you provide the final “spark” needed to convert the gut-produced serotonin into sleep-inducing melatonin.
- Cacao Polyphenols: The polyphenols in cacao protect these delicate neurotransmitters from oxidative stress, ensuring that the serotonin produced in the gut remains stable enough to be utilized by the nervous system.
The “Serotonin-Melatonin” Synergy Table
| Ingredient | Primary Role in the Pathway | Final Outcome |
| Acacia & Inulin | Produce Butyrate | Rescues Tryptophan & stimulates Serotonin enzymes (TPH1). |
| Cacao Powder | Polyphenols & Amines | Protects neurotransmitters and provides Tryptamine. |
| Magnesium | Enzymatic Co-factor | Drives the conversion of Serotonin –> Melatonin. |
Summary of Benefits
By taking this stack in the evening, you are creating a virtuous cycle:
- Evening: Magnesium and cacao calm the nervous system (GABA support).
- Midnight: Peak butyrate production maximizes serotonin levels in the gut.
- Late Night: Magnesium facilitates the conversion of that serotonin into melatonin, deepening your REM and slow-wave sleep cycles.
Can this Stack impact dopamine levels or Executive Function the following morning?
Taking this “super-stack” in the evening doesn’t just improve sleep; it sets a biological stage for enhanced Executive Function and Dopamine efficiency the following morning.
Research from late 2025 emphasizes that the most significant benefits aren’t necessarily “more” dopamine, but rather a more sensitive and efficient dopamine system.
1. Dopamine: Synthesis and Sensitivity
The combination of SCFAs and Magnesium creates a “dual-trigger” for your reward and motivation system.
- The “D2” Sensitivity Boost: Recent 2025 studies on the Gut-Brain Axis show that butyrate (from your acacia and inulin) crosses the blood-brain barrier and binds to G-protein coupled receptors. This process has been found to increase the expression and sensitivity of Dopamine D2 receptors.
- The Morning Result: You don’t need as much “stimulation” (like caffeine) to feel motivated, because your brain is more responsive to its own natural dopamine.
- The Enzymatic Catalyst: Magnesium is a required co-factor for Tyrosine Hydroxylase, the rate-limiting enzyme that converts L-Tyrosine into dopamine.
- The Morning Result: By morning, your “dopamine reserves” are replenished, preventing that mid-morning motivation crash.
2. Executive Function: The Prefrontal Cortex Connection
Executive Function (EF) – which includes problem-solving, planning, and working memory – is primarily housed in the Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex (DLPFC).
- Cacao and Cerebral Blood Flow (CBF): Cacao flavanols (specifically epicatechin) have a unique ability to improve “vasodilation” in the brain. 2024 fMRI studies show that even 12 hours after consumption, there is a measurable increase in blood flow to the DLPFC.
- Reduced “Cognitive Effort”: Research suggests that cacao polyphenols allow the brain to use resources more efficiently. In “Traffic Light” cognitive tests, participants who consumed cacao the night before showed quicker reaction times with lower recorded brain activity, meaning the brain didn’t have to work as hard to perform complex tasks.
3. The “Morning After” Resilience
The reason this stack is more effective than a morning supplement is the reduction in neuro-inflammation that occurs while you sleep.
- Morning Brain Fog: Often caused by “microglial priming,” where the brain’s immune cells are slightly overactive.
- The Stack’s Fix: 1. Magnesium blocks NMDA receptors, preventing “excitotoxicity” (over-firing of neurons) overnight.
2. Butyrate (peaking around 2:00 AM) “calms” the microglia.
3. Result: You wake up with “Cognitive Resilience” – the ability to handle high-stress or high-complexity tasks (like content creation or deep research) without feeling mentally fatigued by 10:00 AM.
Summary Table: Morning Cognitive Benefits
| Ingredient | Biological Lever | Morning Outcome |
| Acacia & Inulin | SCFA / Butyrate Production | D2 Receptor Sensitivity: Higher motivation and “drive” for the first task of the day. |
| Cacao Powder | Flavanols / Polyphenols | Prefrontal Blood Flow: Faster processing speed and better “Working Memory.” |
| Magnesium | Enzyme Co-factor | Neuro-Stability: Reduced “jittery” focus; more calm, sustained concentration. |
By integrating acacia fiber, inulin, cacao, and magnesium into a consistent evening routine, you are doing far more than just supplementing your diet; you are strategically engineering your internal chemistry for systemic repair. This “super-stack” leverages the unique fermentation lag of soluble fibers to flood your system with butyrate precisely when your body enters its most critical window for hormonal release and neurological “cleanup.” By calming neuro-inflammation, optimizing the serotonin-to-melatonin conversion, and sharpening your dopamine sensitivity for the following morning, this protocol transforms the gut into a powerful engine for both physical resilience and cognitive clarity. Embracing these soluble fibers is an investment in your “biological infrastructure,” providing the essential fuel your microbiome needs to lower the volume on chronic pain and unlock a more focused, motivated version of yourself every single day.

Leave a Reply